Reading environment variables
You can read environment variables directly from process.env in your Gram Functions. Preconfigured values defined in envSchema can also be accessed from ctx.env in the Functions Framework:
import { Gram } from "@gram-ai/functions";
import * as z from "zod/mini";
const gram = new Gram({
envSchema: {
SCHEMA_VALUE: z.string(),
},
}).tool({
name: "fetch_data",
description: "Fetch data from an external API",
inputSchema: { endpoint: z.string() },
async execute(ctx, input) {
const arbitraryValue = process.env.ARBITRARY_VALUE;
const schemaValue = ctx.env.SCHEMA_VALUE;
const response = await fetch(`${arbitraryValue}/${input.endpoint}`);
return ctx.json(await response.json());
},
});
export default gram;Declaring environment variables with envSchema
You can set up environment variables that end users will provide using envSchema. Environment variables specified in the envSchema can be provided by MCP users via headers or via Gram environments.
Using the Functions Framework
Declare environment variables using envSchema in the Functions Framework:
import { Gram } from "@gram-ai/functions";
import * as z from "zod/mini";
const gram = new Gram({
envSchema: {
API_KEY: z.string(),
BASE_URL: z.string().url(),
},
}).tool({
name: "api_call",
inputSchema: { endpoint: z.string() },
async execute(ctx, input) {
const baseUrl = ctx.env.BASE_URL;
const apiKey = ctx.env.API_KEY;
const response = await fetch(`${baseUrl}/${input.endpoint}`, {
headers: { Authorization: `Bearer ${apiKey}` },
});
return ctx.json(await response.json());
},
});
export default gram;Using the MCP SDK
Declare environment variables using the variables option with the MCP SDK wrapper:
import { withGram } from "@gram-ai/functions/mcp";
import { server } from "./mcp.ts";
export default withGram(server, {
variables: {
API_KEY: { description: "API key for authentication" },
BASE_URL: { description: "Base URL for the API" },
},
});Attaching environments to Functions in Gram
To attach an environment to your Gram Function, first ensure you have created an environment with the configuration values you want to attach.
Then follow these steps:
-
Navigate to the Toolsets tab.
-
Click the More Actions () menu on the Source Card for your Gram Function.
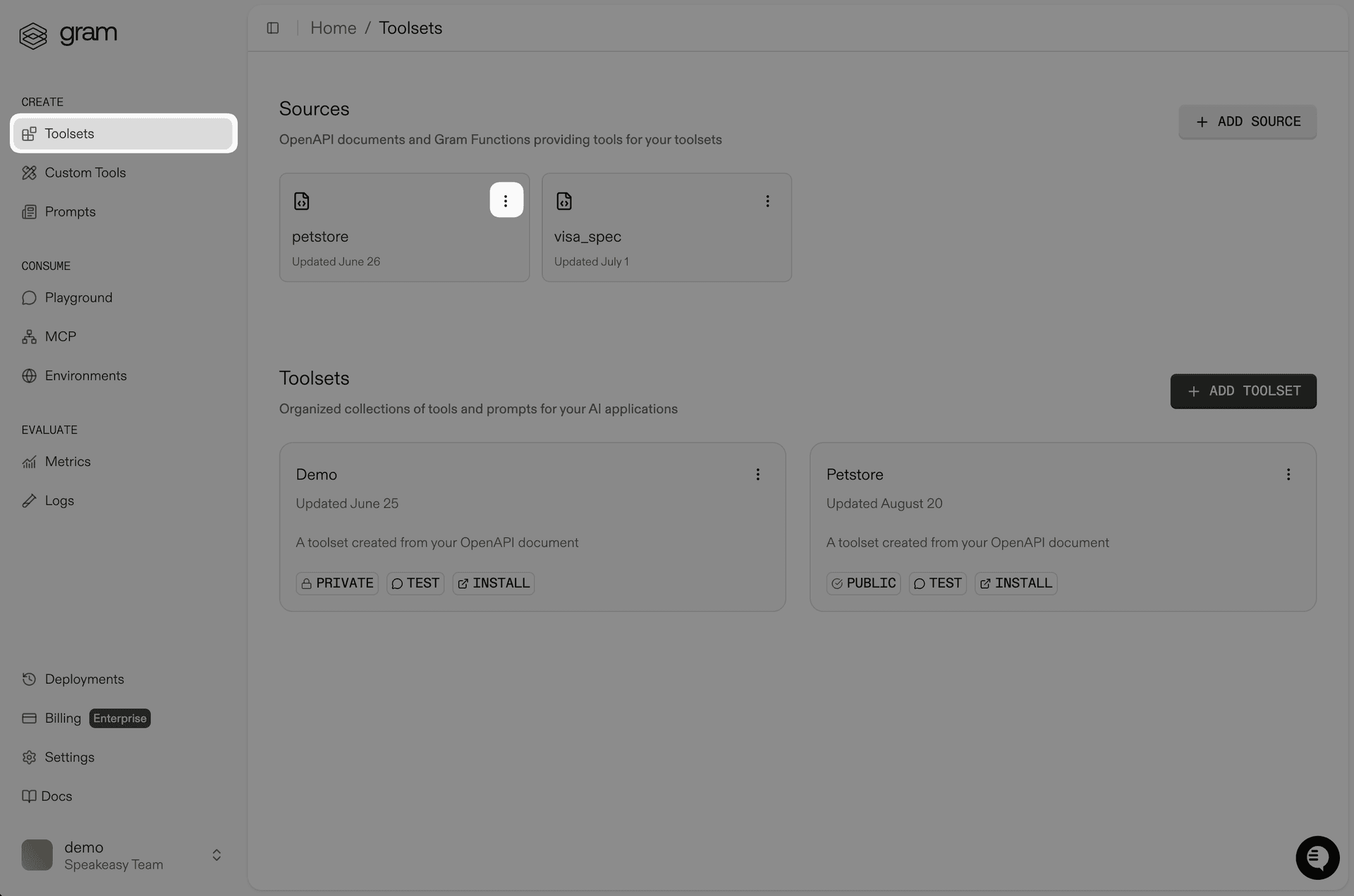
-
Click Attach Environment.
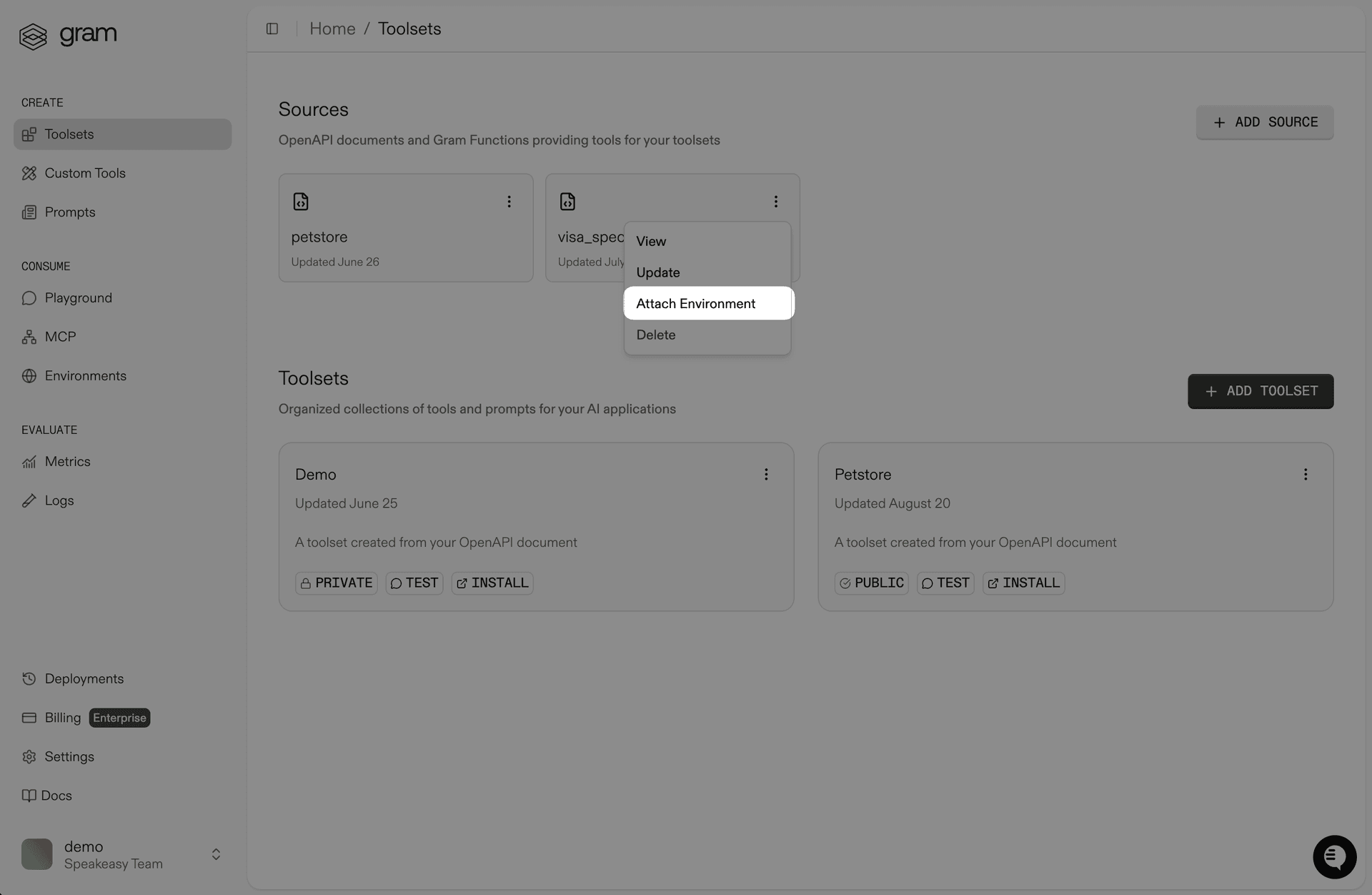
-
Select the environment you created in the first step.
These environment values will now apply to all users of the Function.
Warning
A configuration attached to a Function source will apply to all users, including users of public MCP servers. Be careful not to include user-specific credentials or tokens that should only be available to certain users.
Providing environment configuration from clients
If you have a Gram API key, you can provide that key and a GRAM_ENVIRONMENT header set to the slug for your environment. For an example of using environments with the Gram SDKs, see the guide to using environments with the Vercel AI SDK.
You can also configure your MCP client to send headers with environment configurations. For more information, check the documentation for installing your MCP server on the client of your choosing.
Last updated on